Conversions
1litre= .001 cubic meter1m^3=1000litres
1BTU(british thermal unit) = 1055 joules
1 btu/hr=3.412 joules/s
Area
100 cents = 1 Acre
1 Acre = 4840 sq yards
1 yard = 3' or 36"
1 cents = 435.60 sq ft
1 sq. m = 10.76 sq. ft
1 Acre= 4047 sq m
2,47 cents = 1 are(100 sq meter)
2.47 acres = 1 hectare(10,000 sq meters)
Fibonacci series
Fn= Fn-1 + Fn-2
0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21....
Golden Ratio

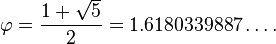
Slope/ Gradient
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grade_(slope)
Contour interval: the difference in altitude represented by the space between two contour lines on a map
PERT- Te(expected time)= (O +4M + P)/6 where O=optimistic time, M= most likely time, P=pessimistic time.
V(variance)=( (P-O)/6)^2
Project variance= sum of variances along the critical path
Standard deviation = sq root of variance
unit mass of reinforced concrete= 2400kg/m3
unit wt of reinfirced concrete= 2400 * 10(9.8)N/m3
density of steel = 7850kg/m3
BM and SF diagram
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q0DghZBR-AUHooks Law, Young;s Modulus, Bulk Modulus, Poisson's Ratio
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QMmOMLstGm0Scale of Aerial Photograph = Focal length/ Altitude above Ground level
Forecasting Population
Arithmatic method
dP/dt = Ka
P = P1 + Ka (t - t1)
P = population
t = time
Ka =
arithmetic growth constant
Geometric method
dP/dt= KgP
lnP = lnP1 + Kg (t - t1)
Kg =lnP2-lnP1/t2-t1 = ln[P2/P1]/t2-t1
P = population
t = time
Kg =
geometric growth constant
Note: lim (1+K)1/K = e = 2.718… base of the natural logarithms
K®0
1 lux = 1 lumen/sq meter
lux is the unit of illuminance
Flux= illumination required(lux) x surface area(sq m)
Flux(lumen output)(received)= MF(maintenance factor) x UF(utilization factor) x Flux(installed)
depreciation factor = reciprocal of maintenance factor
lux=candela/d^2
cd(candela) = lm(lumen) / ( 2π(1 - cos(º/2)) )
for isotrophic light source(all directions), lumen = candela x 4x22/7
http://www.compuphase.com/electronics/candela_lumen.htm
Room Index(RI)= Lx W/[Hm x (L+W)]
Hm=mounting height
Spacing to height ratio SHR= 1/Hm x[ (A/N)^ 1/2]
Acoustics
T(reverbaration time in seconds)= .161x V(volume in m3)/A(sound absorption power in m2-sabine = area x coeffcient of absorption)
Lp = 20 log 10(Prms/Pref) dB
Lp2 = Lp1 + 20 log10(r1/r2)
lp-sound pressuresound level- 10 log 10(Prms/Pref) dB
Norris Eyring Formula

Lp= Lw-10.log4πr2
The handling capacity(lifts) is calculated by the
formula: H= 3OOxQx100 /TXP
where
H = handling capacity as the percentage of the peak population handled during 5 min period,
Q = average number of passengers carried in a car,
T = waiting interval, and
P = total population to be handled during peak morning period. (It is related to the area served by a particular bank of lifts.)
The value of ‘Q’ depends on the dimensions of the car. It may be noted that the car is not loaded always to its maximum capacity during each trip and, therefore, for calculating ‘H” the value of ‘Q’ is taken as 80 percent of the maximum carrying capacity of the car.
The waiting interval is calculated by the formula:
T= RTT/N
iv
where
T = waiting interval;
N = number of lifts, and
RTT= round trip time, that is, the average time required by each lift in taking one full load of passengers from ground floor, discharging them in various upper floors and coming back to ground floor for taking fresh passengers for the next trip.
Thermal transmittance, also known as U-value, is the rate of transfer of heat (in watts) through one square metre of a structure divided by the difference in temperature across the structure. It is expressed in watts per metres squared kelvin, or W/m²K. Well-insulated parts of a building have a low thermal transmittance whereas poorly insulated parts of a building have a high thermal transmittance.
- Φ = A × U × (T1 - T2)
The formula for ventilation heat loss is:
Q = N . V . Sp.ht . dt
Where;
Q = heat loss (Watts) (W)
N = Number of air changes per hour. An air change is one room volume.
V = Room volume (m3)
Sp.ht. = Specific heat factor for air. This is found from the following formula.
Sp. Ht. Factor = ( Specific heat capacity of air x 1000 to convert from kJ to Joules x density of air ) / 3600 to convert from hr to secs.
Sp. Ht. Factor = (1.01 x 1000 x 1.2 ) / ( 3600 )
Sp. Ht. Factor = 0.34
dt = temperature difference between inside and outside (oC)
Duct cross sectional area A(m2)= q(air flow rate m3/s)/v(air speed m/s)
Traffic formulas
q(flow=no vehicles /time)=1/h(time headway=time between rear bumper to rear bumper)
density k=n/distance(number of vehicles occupying a given lengthnof highway
distance headway= distance between corresponding points in two successive vehicles
k(density)=1/s(distance headway)
Plumbing and Water Supply
Hazen -Williams Formula
used for pipes larger than 2" and smaller than 6' in dia
v = 1.32.Ch.R^0.63.S^0.54
v= average velocity ft/s
Ch=Hazen Williams Coefficient
R=Hydraulic radius of flow conduit(ft)
s=ratio of hL/L, energy loss/head lenghth of conduit(ft/ft)
in SI Units
v = 0.85.Ch.R^0.63.S^0.54
v= average velocity(m/s)
Ch=Hazen Williams Coefficient
R=Hydraulic radius of flow conduit(m)
s=ratio of hL/L, energy loss/head lenghth of conduit(m/m)
Volume flow rate Q= Av
Ammortisation formula for sinking fund
Compound Interest
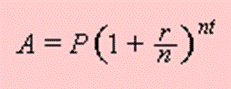
r= rate of interest as decimal
n= no of times interest is compounded in ayear
t= no of years

Thank you.
ReplyDeleteIt's very useful :D
all the best!
DeleteTHANKU SO MUCH...
ReplyDeleteCan you give me gate 2012 solved paper
Deletethanks a lot..
ReplyDeleteare these formulas sufficient for solving the problems?
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletecould y plz update the blog as the syllabus for gate 2016 has been changed a little bit
ReplyDeleteI have updated it. Thanks for letting me know!
DeleteHi mam,As iisc is conducting exam this tym and ur a student of iisc could u plz tell which part of syllabus will be more focussed :)
DeleteIISc does not have an architecture department. Even if it had,that kind of information would be confidential. But generally, I have heard that they are planning to make the exams more numerical oriented(where you have to enter the value as opposed to selecting from options) for all branches, but really cant say...
DeleteThanks fr ur reply i will make sure to cover all numericals :)
DeleteYour blog is very informative and motivational. Thanks for sharing your experience. You are an educator in true sense :)
ReplyDeletethank you
ReplyDeletethank u mentor
ReplyDeletethank u mentor
ReplyDeletethanku its a saviour
ReplyDeleteThank you
ReplyDeleterly thankful for your effort to include all the necessary details required within a short time!!
ReplyDeleteSuper Thanks
ReplyDeleteThank you very much for the information.
ReplyDeleteuseful info thank u:)
ReplyDeletevery help full
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletethe information provided here is very helpful for the preparations...its just a request if some more details and calculation techniques regarding sewage and septic tank calculations can be added, as i am not getting any such concrete formula regarding it...
ReplyDeletethank you
Can u recommend any book or link for the traffic and transport management? Also from where I can find septic tank calculations ?
ReplyDeletethe information above is very useful..can u pls guide me from where to start preperation for gate 2018.i m bit confused..i mean from previous years question paper, or from syllabus and to gradually proceed..it will be really helpful
ReplyDeletedo you have any relevant data for gate 2018?
Deleteplease send me as well
shivikamehrotra6@gmail.com
http://www.onlineicegate.com ICE GATE is a GATE TRAINING INSTITUTE and is being considered as BEST ONLINE GATE COACHING. It is GATE TRAINING CENTER offering best Books for Gate .
ReplyDeleteThank you Sonia.
ReplyDeleteI would like to know about good study material used by students for Gate.
Kindly help if anyone knows.
i am studying in 4th year starting my internship in january. when is the right time to start preparing?
ReplyDeleteNice! Thanks!
ReplyDeleteHello,
ReplyDeleteIt is possible for a gate aspirant to prepare for the bank exam.
bank Exam aspirant